Environmental Justice Index
To evaluate the overall distribution of air pollution-associated health burdens across communities with different vulnerabilities, a Lorenz Curve-based method is applied to measure the distribution's inequality level, namely the Environmental Justice Index (EJI). Similar to the Gini factor used to measure income/distribution disparity, the Environmental Justice Index ranks the population accumulation curve based on the corresponding SVI value instead of the value of the target distribution.
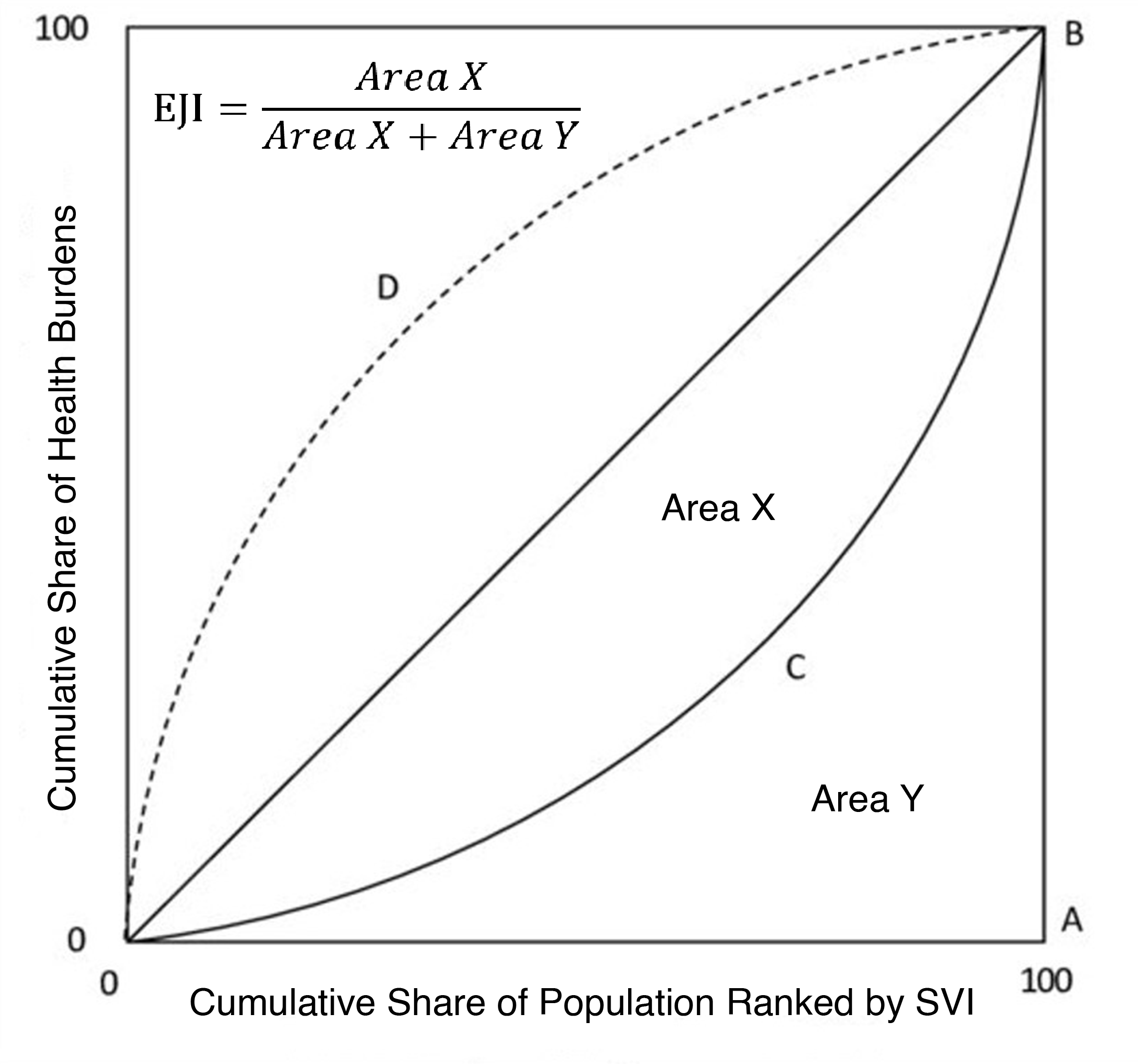
The code used for the calculation of EJI in the paper "Improvements in U.S. Air Quality have not Addressed Pollution Inequalities - Especially among Minority and Elderly Populations" can be found here Python_Code_for_EJI. The code for mortatlity dataset preprocessing is here Python_Mortality_Preprocessing. For more technical details, please contact: sz@apep.uci.edu
The mortality datasets for code inputs can be accessed through the public link: https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/EZ5P2.